Sonography & Antenatal Scanning
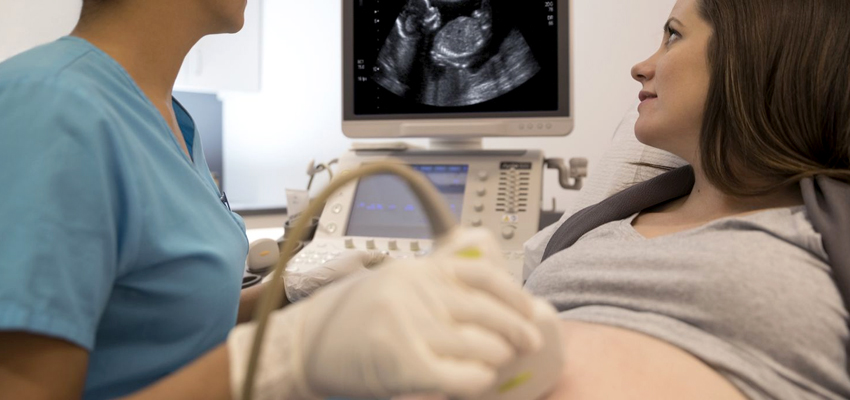
Sonography, also known as ultrasound imaging, is a medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce real-time images of the body's internal structures. Sonography is commonly used in various medical specialties, including obstetrics and gynecology, to visualize and evaluate the organs and tissues within the body.
In the context of antenatal care, sonography plays a crucial role in monitoring the development and health of the fetus during pregnancy. Antenatal scanning, also known as prenatal ultrasound, involves using ultrasound technology to assess the growth, anatomy, and well-being of the fetus in the womb.
Antenatal scanning can provide valuable information about the following aspects of fetal development:
-
Gestational age: Ultrasound measurements, such as crown-rump length (CRL) or biparietal diameter (BPD), can help determine the gestational age of the fetus and estimate the due date.
-
Fetal anatomy: Detailed ultrasound scans, typically performed during the second trimester (around 18-20 weeks of pregnancy), allow healthcare providers to examine the fetal anatomy and detect any structural abnormalities or congenital anomalies.
-
Fetal growth: Serial ultrasound measurements of fetal biometry, including head circumference, abdominal circumference, and femur length, can assess fetal growth and detect growth abnormalities, such as intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) or macrosomia.
-
Placental location and function: Ultrasound imaging can evaluate the position and function of the placenta, including detecting placenta previa (when the placenta partially or completely covers the cervix) or placental insufficiency (when the placenta is unable to adequately support fetal growth).
-
Amniotic fluid volume: Ultrasound can assess the volume of amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus, helping to diagnose conditions such as oligohydramnios (low amniotic fluid) or polyhydramnios (excessive amniotic fluid).
Antenatal scanning is a safe and non-invasive procedure that does not involve ionizing radiation, making it suitable for routine use during pregnancy. It allows healthcare providers to monitor the progress of the pregnancy, identify any potential complications, and provide appropriate interventions or management as needed to optimize maternal and fetal health.
Overall, sonography and antenatal scanning play a vital role in prenatal care by providing valuable information about fetal development and helping to ensure the best possible outcomes for both mother and baby.